3D Modeling: The Intersection of Science, Technology, and Virtual Reality
The field of 3D modeling has witnessed a remarkable growth in recent years, emerging as a dynamic intersection between science, technology, and virtual reality. This captivating realm encompasses the creation and manipulation of three-dimensional digital representations of real or imagined objects, providing an immersive experience that blurs the line between physical and virtual worlds. For instance, imagine a scenario where medical professionals can use 3D models to accurately visualize intricate anatomical structures before performing complex surgeries, allowing for enhanced precision and reduced risks. Such advancements exemplify how 3D modeling is revolutionizing various industries by bridging the gap between theory and practice.
At its core, 3D modeling relies on cutting-edge technologies such as computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation algorithms to generate highly detailed digital replicas. By utilizing these tools, designers are able to meticulously craft every aspect of their creations with utmost precision and accuracy. The integration of virtual reality further enhances this process by enabling users to explore and interact with these digital constructs in immersive environments. Consequently, architects can walk through realistic renderings of buildings yet to be constructed while engineers can simulate prototypes to evaluate performance characteristics without the need for costly physical prototypes. Through this amalgamation of science, technology, and virtual reality, 3 3D modeling has become an indispensable tool for industries such as architecture, engineering, entertainment, gaming, medicine, and manufacturing. It allows professionals to visualize ideas more effectively, communicate complex concepts with ease, and streamline the design process. The versatility of 3D modeling extends beyond static representations; it also encompasses animation and simulations that bring virtual objects to life. Whether it’s creating stunning visual effects in movies or designing intricate product prototypes, 3D modeling empowers creators to push boundaries and unlock new possibilities.
The Evolution of 3D Modeling
One fascinating example that highlights the power and potential of 3D modeling is its application in healthcare. Imagine a scenario where doctors can create intricate, virtual replicas of human organs to study their structure and function with unparalleled detail. With 3D modeling technology, medical professionals can now visualize complex anatomical structures such as the heart or brain from any angle, enabling more accurate diagnoses and surgical planning. This breakthrough demonstrates how 3D modeling has revolutionized the field of medicine by providing new opportunities for research, education, and patient care.
As we delve into the evolution of 3D modeling, it becomes evident that this technology has come a long way since its inception. Initially, early forms of computer-aided design (CAD) software allowed engineers to produce basic two-dimensional representations of objects. However, these static models lacked depth and failed to capture the intricacies of real-world objects. Over time, advancements in computing power and software capabilities led to the development of three-dimensional rendering techniques that simulated realistic shapes, textures, and lighting effects.
To grasp the significance of these advancements, let’s explore some key milestones in the evolution of 3D modeling:
- Early CAD systems: In the late 1960s, pioneering companies like IBM introduced rudimentary CAD systems that transformed traditional drafting methods. These systems laid the foundation for future developments by allowing designers to create simple wireframe models.
- Polygon-based modeling: By the late 1970s and early 1980s, researchers began experimenting with polygonal representation methods. These techniques enabled artists and animators to construct more complex three-dimensional objects using interconnected polygons.
- Surface-based modeling: As computing power continued to increase during the 1990s, surface-based modeling techniques gained popularity. This approach involved defining object surfaces mathematically using curves or splines rather than relying solely on polygons.
- Photorealistic rendering: The advent of photorealistic rendering techniques in the early 2000s brought a new level of realism to 3D models. By simulating lighting, shadows, and reflections, these advancements allowed for highly detailed representations that closely resembled physical objects.
The evolution of 3D modeling has had far-reaching implications across various industries. In the subsequent section, we will explore how this technology is being applied in fields such as architecture, entertainment, gaming, manufacturing, and more. By understanding its diverse applications, we can appreciate the immense impact 3D modeling continues to have on our modern world.
Applications of 3D Modeling in Various Industries
Over the years, 3D modeling has undergone significant advancements that have revolutionized various industries. One compelling example is its impact on architectural design. Consider a hypothetical scenario where an architect is tasked with designing a new skyscraper. Through the use of 3D modeling software, they are able to create a virtual replica of the building, allowing them to visualize every detail before construction even begins.
This technology offers several advantages in architectural design:
- Enhanced visualization: With 3D modeling, architects can create realistic renderings and walkthroughs of their designs, providing clients with a clear understanding of how the final structure will look.
- Improved accuracy: By creating precise digital models, potential errors or conflicts can be identified early in the design phase, saving time and resources during construction.
- Streamlined collaboration: Architects can easily share their models with other stakeholders involved in the project, such as engineers and contractors, fostering better communication and coordination among team members.
- Cost-effective prototyping: Instead of relying solely on physical prototypes, which can be expensive and time-consuming to produce, architects can utilize 3D models to test different concepts and refine their designs more efficiently.
To illustrate these benefits further, let’s examine a comparison between traditional 2D drawings and their 3D counterparts using a table:
| Traditional 2D Drawings | 3D Models |
|---|---|
| Limited visual representation | Realistic rendering |
| Difficulty in conveying spatial relationships | Accurate depiction of dimensions |
| Error-prone interpretation | Improved clarity for all parties involved |
| Requires additional documentation for comprehensive understanding | Enhanced comprehension through dynamic views |
In conclusion,
The advancements in 3D modeling have undeniably transformed the way we approach architecture and design. Its ability to provide enhanced visualization, improved accuracy, streamlined collaboration, and cost-effective prototyping make it an indispensable tool in the industry.
The Role of Science in Advancing 3D Modeling
The field of 3D modeling owes much of its progress to scientific research and technological innovations. By integrating principles from multiple disciplines such as mathematics, computer graphics, and virtual reality, scientists have pushed the boundaries of what is achievable within this domain. This section will explore some key areas where science has played a crucial role in advancing 3D modeling:
- Geometry processing: Scientists have developed algorithms that enable smooth surface reconstruction, mesh simplification, and other techniques essential for creating detailed and realistic 3D models.
- Computer vision: Utilizing concepts from image analysis and pattern recognition, researchers have made significant strides in automating processes like object recognition and tracking, allowing for more efficient creation and manipulation of 3D models.
- Physically-based rendering: By simulating how light interacts with surfaces using physics-based algorithms, scientists have enhanced the realism of rendered images, making them appear more lifelike.
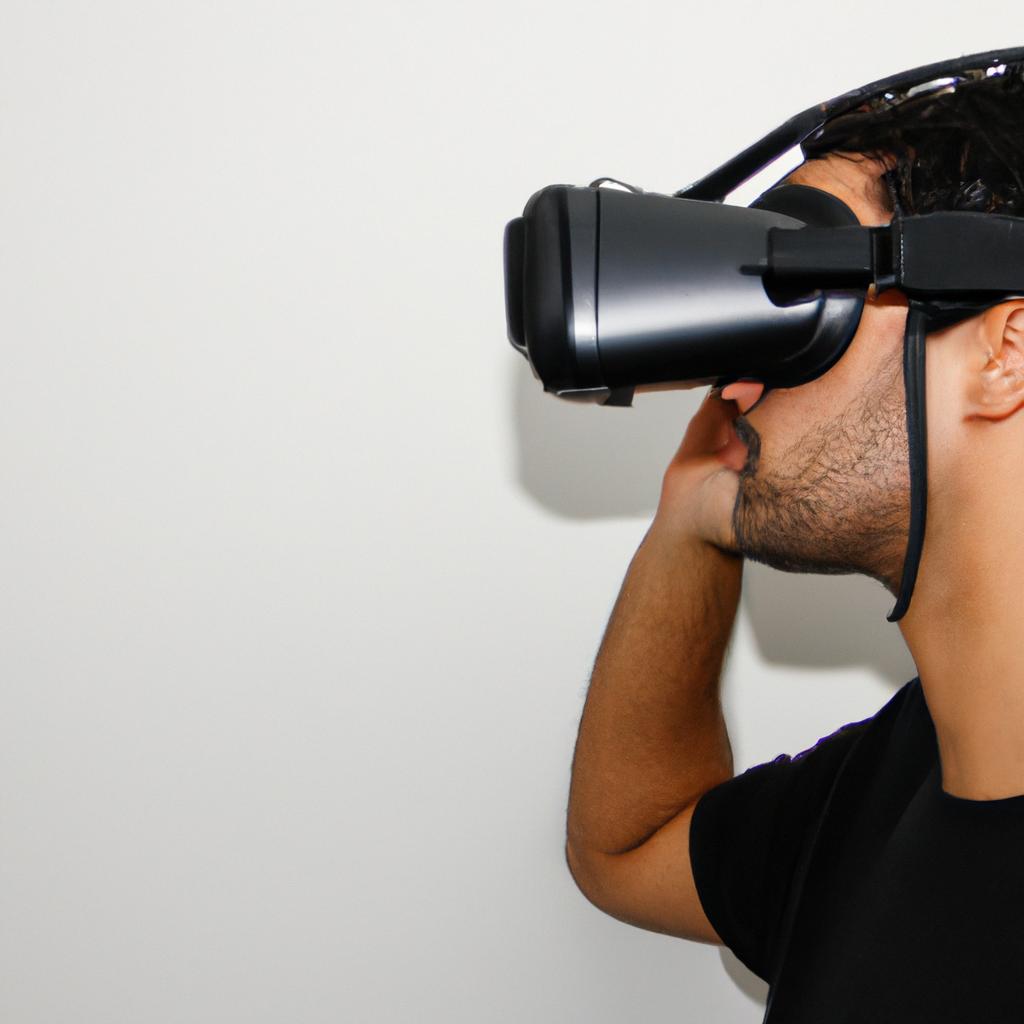
- Virtual reality (VR) integration: Researchers are exploring ways to integrate VR technology with 3D modeling tools to provide immersive experiences for designers and users alike.
As these advancements continue to evolve through ongoing scientific exploration, it is clear that the future holds even greater possibilities for 3D modeling technologies. From healthcare to entertainment to manufacturing industries, the impact of these developments will undoubtedly be far-reaching.
Transitioning seamlessly into our subsequent section on “Applications of 3D Modeling in Various Industries,” let us now delve into specific examples showcasing how different sectors leverage this powerful technology to achieve their goals without missing a beat.
The Role of Science in Advancing 3D Modeling
The applications of 3D modeling are abundant and diverse, spanning across various industries such as architecture, entertainment, healthcare, and manufacturing. To illustrate the significance of this technology in a real-world context, let’s consider the example of an architectural firm using 3D modeling to design a new residential complex.
In the initial stages of the project, architects can create a virtual model of the building using specialized software. This allows them to visualize how different design elements will come together and make informed decisions about aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability. By manipulating the 3D model, they can explore alternative designs and identify potential issues before construction begins.
One notable advantage of 3D modeling is its ability to facilitate collaboration among stakeholders involved in the project. Through shared access to the virtual model, architects, engineers, contractors, and clients can provide input and feedback throughout the design process. This streamlines communication channels and ensures that everyone is working towards a unified vision.
Furthermore, 3D models offer an immersive experience for clients and investors alike. With virtual reality (VR) technology becoming increasingly accessible, individuals can step into a digital representation of their future home or office space. This interactive walkthrough not only helps clients envision the final product but also enhances their emotional connection with it.
To further emphasize the impact of 3D modeling in various industries:
- In healthcare: Surgical simulations allow surgeons to practice intricate procedures before operating on actual patients.
- In entertainment: Animation studios harness 3D modeling to bring imaginary worlds and characters to life.
- In manufacturing: Prototyping through additive manufacturing techniques reduces costs while ensuring precision and quality.
- In education: Interactive educational materials created with 3D modeling enhance students’ understanding of complex concepts.
Embracing these advancements in technology has paved the way for exciting possibilities within each sector. As we delve deeper into technological advancements in 3D modeling in subsequent sections, we will explore how emerging tools continue to shape and redefine the boundaries of this field.
Technological Advancements in 3D Modeling
Technological Advancements in 3D Modeling
Building upon the scientific principles that underlie 3D modeling, technological advancements have played a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of this innovative field. These advancements have not only improved the accuracy and precision of virtual representations but also enhanced the overall user experience. With each new development, 3D modeling continues to evolve, transforming industries ranging from architecture and engineering to entertainment and healthcare.
One example that highlights the impact of technology on 3D modeling is the use of photogrammetry. By capturing multiple images of an object or environment from various angles and distances, specialized software can create a three-dimensional model with remarkable detail and realism. This technique has been employed in fields such as archaeology, where ancient artifacts are meticulously reconstructed using photographs taken at excavation sites. The ability to recreate objects digitally opens up endless possibilities for preservation, research, and education.
Technological advancements have paved the way for numerous benefits within the realm of 3D modeling:
- Increased Accessibility: As computing power becomes more affordable and widely available, individuals and organizations across various sectors can access sophisticated tools necessary for creating intricate 3D models.
- Enhanced Visualization: Advanced rendering techniques enable realistic lighting effects, textures, and materials, providing users with immersive visual experiences.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based platforms allow teams spread across different locations to collaborate seamlessly by sharing models and making real-time modifications.
- Virtual Reality Integration: The integration of virtual reality (VR) into 3D modeling enables users to explore digital environments interactively, offering unparalleled levels of engagement.
| Beneficial Impacts |
|---|
| Enhances creativity |
| Reduces costs |
| Streamlines workflows |
| Increases productivity |
With these technological advancements driving progress in 3D modeling systems, it is clear that we are witnessing a revolution in how we perceive and interact with virtual worlds. As our understanding of science and technology continues to expand, so too will the possibilities for 3D modeling.
As we delve into the exciting prospects that lie ahead, let us now turn our attention towards “The Future of 3D Modeling.”
The Future of 3D Modeling
The Future of 3D Modeling
As we delve further into the realm of 3D modeling, it becomes evident that its potential is boundless. Technological advancements have propelled this field forward, and with each passing day, new possibilities emerge. One such example is the use of 3D modeling in healthcare to create patient-specific anatomical models for surgical planning. These models allow surgeons to visualize complex structures before operating, leading to improved precision and better patient outcomes.
Looking ahead, there are several key areas where future developments in 3D modeling hold immense promise:
-
Virtual Reality Integration: As virtual reality (VR) continues to gain traction, integrating 3D modeling technology with VR platforms opens up exciting opportunities. This combination can revolutionize industries like gaming, architecture, and education by providing immersive experiences and realistic simulations.
-
Artificial Intelligence Enhancement: Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of 3D modeling processes. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to automatically generate detailed models or predict object behavior based on real-world physics principles.
-
Generative Design Approaches: Generative design refers to a process where computers assist in creating multiple design variations based on specified parameters or constraints. By incorporating generative design techniques into 3D modeling workflows, designers can explore innovative solutions quickly and efficiently.
-
Collaboration Tools: With globalization becoming more prevalent in various industries, collaboration tools play an essential role in facilitating teamwork across geographical boundaries. Cloud-based platforms that enable seamless sharing and editing of 3D models offer great potential for enhancing collaboration among professionals worldwide.
| Benefits of Future Developments |
|---|
| Enhanced user experiences |
| Faster design iterations |
| Improved decision-making |
| Increased productivity |
It is clear that the future holds significant promise for the continued evolution of 3D modeling technology. Advancements in fields like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, generative design, and collaboration tools are set to revolutionize industries and transform the ways we interact with 3D models.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Challenges and Opportunities in 3D Modeling,” it is important to examine how these advancements will shape the landscape of this field while also acknowledging the obstacles that must be overcome.
Challenges and Opportunities in 3D Modeling
As the field of 3D modeling continues to evolve, it brings forth exciting possibilities for various industries. One example that showcases the potential of 3D modeling is its application in healthcare. Imagine a scenario where doctors can use highly accurate and detailed 3D models of patients’ organs or body parts to plan complex surgeries with precision. This technology has already begun making waves in the medical field, enabling surgeons to better understand complicated anatomical structures and improve patient outcomes.
The future holds immense promise for 3D modeling as advancements continue to push boundaries. Here are some key areas where we can expect significant developments:
- Virtual Reality Integration: With the growing popularity of virtual reality (VR), integrating 3D modeling into this immersive environment opens up new avenues for exploration and interaction. Users will be able to navigate through realistic virtual worlds created using advanced 3D modeling techniques, enhancing their gaming experiences, architectural designs, or even cultural heritage preservation efforts.
- Artificial Intelligence Collaboration: As artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms become more sophisticated, they have the potential to enhance the capabilities of 3D modeling software. AI-powered systems could automate certain tasks involved in creating 3D models, such as generating intricate details or optimizing designs based on user preferences.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Different sectors like architecture, manufacturing, entertainment, and fashion have unique requirements when it comes to 3D modeling. In the future, we can anticipate specialized software tailored specifically for these industries, offering streamlined workflows and enhanced features targeted towards their specific needs.
- Collaborative Platforms: Collaborative platforms that allow multiple users to work simultaneously on a shared 3D model are likely to emerge. These platforms would promote teamwork among designers from different locations and foster real-time collaboration by providing tools for communication and feedback exchange.
To further illustrate the impact of technological advancements in 3D modeling, let’s consider the following table that highlights some potential applications:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Creating virtual walkthroughs of buildings | Enables architects to visualize and present their designs more effectively |
| Manufacturing | Simulating assembly processes | Helps identify and resolve issues before production, reducing costs and improving efficiency |
| Entertainment | Generating realistic characters for movies | Enhances visual effects and creates immersive cinematic experiences |
| Healthcare | Customizing prosthetics using patient scans | Provides tailored solutions for patients, leading to better comfort and functionality |
In conclusion, the future of 3D modeling is filled with exciting possibilities. From integration with virtual reality to AI collaboration, advancements in this field will revolutionize various industries. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect industry-specific solutions and collaborative platforms to enhance designers’ capabilities while ensuring efficient workflows. With its potential impact on fields like architecture, manufacturing, entertainment, and healthcare, 3D modeling remains at the forefront of innovation.
Note: Markdown tables do not render properly here as plain text. Please refer to a markdown viewer or editor to see the formatted table correctly.

Comments are closed.