The Evolution of Science and Technology: The Internet of Things
The evolution of science and technology has brought about significant advancements that have revolutionized various aspects of human life. One such advancement is the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to the network of interconnected devices capable of sharing data and performing tasks without direct human intervention. This article aims to explore the development and impact of IoT, examining its potential applications in different sectors.
To illustrate the significance of IoT, consider a hypothetical scenario where an individual’s home is equipped with smart appliances connected through an IoT network. Upon waking up, the person’s alarm clock triggers a series of events: it communicates with their sleep tracker device to analyze their sleeping patterns, adjusts the lighting in the bedroom accordingly to simulate natural sunlight, and brews coffee based on personalized preferences saved in their smartphone application. As the day progresses, this interconnected system continues to collect data from multiple sources within and outside the house, enabling automated adjustments in temperature control, energy consumption optimization, security monitoring, and even grocery shopping replenishment. Such seamless integration between devices exemplifies how IoT can enhance convenience and efficiency in daily activities.
As we delve deeper into understanding the evolution of science and technology regarding IoT, it becomes evident that this concept extends beyond personal homes. The transformative potential lies in its ability to connect entire cities, industries, and ecosystems. In smart cities, IoT can facilitate efficient management of resources such as energy, water, and transportation systems. For instance, sensors deployed throughout the city can monitor traffic flow and adjust signal timings accordingly to minimize congestion. Smart grids powered by IoT technology enable better monitoring and control of electricity distribution, leading to optimized energy usage and reduced costs.
In industries, IoT enables the concept of “Industry 4.0,” where machines and devices are connected to create intelligent manufacturing systems. This connectivity allows for real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance of equipment, and streamlined production processes. IoT also plays a crucial role in supply chain management by enabling tracking and monitoring of goods at every stage, improving efficiency and reducing losses.
Moreover, IoT has significant implications for healthcare. Medical devices equipped with sensors can collect patient data remotely and transmit it to healthcare professionals in real-time. This enables early detection of health issues, remote patient monitoring, and personalized treatment plans. In emergencies or critical situations, IoT-connected medical devices can alert healthcare providers immediately for timely intervention.
The development of 5G networks further amplifies the potential impact of IoT by providing faster data transfer speeds and lower latency. This opens up possibilities for more complex applications like autonomous vehicles or immersive virtual reality experiences.
However, along with its immense benefits come challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption. These include concerns over privacy and security due to the vast amount of personal data being collected and transmitted within an IoT network. Additionally, standards need to be established to ensure interoperability between different devices from various manufacturers.
In conclusion, the evolution of science and technology has led us into the era of IoT – a network of interconnected devices revolutionizing various sectors including homes, cities, industries, healthcare, and more. The potential applications are vast as it enhances convenience, efficiency, resource management capabilities while paving the way for new innovative solutions. As we continue to explore this transformative technology further, addressing challenges and ensuring security will be essential for its successful integration into our daily lives.
Evolution of Data Security
The rapid advancement of technology has brought numerous benefits to our society, particularly in the realm of data security. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), where everyday objects are connected and able to exchange information, there is a growing concern regarding the protection and privacy of personal data. To illustrate this point, consider a hypothetical scenario: an individual’s smart home devices, such as their thermostat, refrigerator, and security system, are all interconnected via the IoT. Without adequate security measures in place, hackers could potentially gain access to these devices and obtain sensitive information about the homeowner’s daily routines or even break into their house.
To address these concerns and safeguard personal data, several key developments have emerged in the field of data security within the context of IoT:
-
Encryption: Encryption plays a crucial role in Protecting Data transmitted through IoT devices. By encoding information using complex algorithms, it becomes virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to interpret or manipulate sensitive data. For instance, when a person remotely adjusts their smart thermostat temperature using a smartphone app, encryption ensures that only authorized users can access and modify this information.
-
Authentication protocols: Robust authentication mechanisms are essential for ensuring that only legitimate users can access IoT devices and their associated networks. This involves implementing secure login processes with unique usernames and passwords or utilizing more advanced methods like biometric identification systems. Through these protocols, potential vulnerabilities arising from weak credentials can be mitigated.
-
Secure firmware updates: Regularly updating device firmware is critical for addressing any discovered security vulnerabilities promptly. Manufacturers must ensure that software patches are released regularly and efficiently distributed to minimize risks posed by previously unknown threats.
-
Privacy regulations: In response to increasing concerns surrounding user privacy in relation to IoT technologies, governments worldwide have implemented various regulations aimed at protecting consumers’ rights. These regulations often require companies to comply with specific standards when handling personal data collected through IoT devices.
This emphasis on data security within the IoT ecosystem not only enhances personal privacy but also promotes trust and confidence in these technologies. By implementing robust encryption, authentication protocols, secure firmware updates, and adhering to privacy regulations, individuals can feel more at ease when utilizing IoT devices.
Looking ahead, advancements in wireless communication will continue to shape the evolution of technology and further enhance our daily lives. With a seamless transition from this discussion on data security, let us now explore the exciting developments in wireless communication that have paved the way for a connected world.
Advancements in Wireless Communication
With the rapid advancement in technology, data security has become a paramount concern for individuals and organizations alike. Ensuring the protection of sensitive information has evolved alongside technological progress to meet the challenges posed by emerging threats. An illustrative example is the case study of a multinational corporation that suffered a major data breach due to vulnerabilities in its network security system.
To effectively combat these risks, several key developments have taken place in the field of data security:
-
Encryption techniques: Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data from unauthorized access. Advanced encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), have been developed to provide stronger protection against potential breaches.
-
Intrusion detection systems: With cyber-attacks becoming increasingly sophisticated, intrusion detection systems have emerged as vital tools for identifying and responding to potential threats. These systems continuously monitor networks and analyze traffic patterns, helping detect any suspicious activities or unauthorized access attempts.
-
Multi-factor authentication: To enhance security measures, multi-factor authentication methods have gained prominence. This involves combining multiple factors, such as passwords, biometrics (e.g., fingerprint scans), and one-time passcodes sent via SMS or email, to verify identity before granting access to critical information.
-
Vulnerability assessments: Regular vulnerability assessments are necessary to identify weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure proactively. By conducting comprehensive assessments periodically, companies can address vulnerabilities promptly and implement appropriate measures to mitigate potential risks.
Table 1 below provides an overview of some essential aspects related to data security:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Threat landscape | Constantly evolving with new attack vectors and sophisticated techniques |
| Compliance standards | Regulatory guidelines dictating how organizations handle sensitive data |
| Incident response | A structured approach to handling cybersecurity incidents |
| User awareness | Educating users about best practices for maintaining data privacy |
The evolution of data security has been driven by the need to protect valuable information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. By implementing robust encryption techniques, intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication methods, and regular vulnerability assessments, organizations can enhance their defense mechanisms against cyber threats.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Automating Homes for Efficiency,” advancements in data security have laid a solid foundation for further innovations in technology-enabled lifestyles.
Automating Homes for Efficiency
Advancements in Wireless Communication have paved the way for a multitude of technological innovations, and one significant outcome is the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices capable of exchanging data seamlessly. This section will delve into how wireless communication technologies have contributed to the growth and development of this transformative concept.
To illustrate its practical application, consider a hypothetical scenario where an individual wakes up in the morning. As they enter their kitchen, the coffee machine automatically starts brewing a fresh cup of coffee based on data received from their alarm clock. Simultaneously, their smart refrigerator sends notifications about low milk supply directly to their smartphone, allowing them to add it to their shopping list conveniently. These seemingly mundane tasks are made possible by leveraging wireless communication protocols within an IoT framework.
The integration of wireless communication technologies has enabled several key developments within the realm of IoT:
- Enhanced connectivity: With advancements like 5G networks, which offer faster speeds and lower latency, devices can communicate with each other more effectively.
- Expanded reach: Wireless communication allows for greater coverage areas, enabling IoT devices to function even in remote locations or challenging environments.
- Improved energy efficiency: Wireless protocols designed specifically for IoT Applications minimize power consumption, ensuring that connected devices operate efficiently without draining excessive energy.
- Seamless integration: By utilizing standardized wireless protocols, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), different manufacturers’ IoT devices can communicate effortlessly with each other across various ecosystems.
This table provides an overview of some common wireless communication technologies utilized in IoT systems:
| Technology | Range | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Short-medium range | High bandwidth |
| Zigbee | Short range | Low-medium bandwidth |
| Z-Wave | Short range | Low-medium bandwidth |
| LoRaWAN | Long range | Low bandwidth |
The advancements in wireless communication have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, enabling a seamless integration of various devices and systems. As IoT continues to evolve, it opens up new possibilities for automation, convenience, and efficiency in our daily lives.
Transitioning to the next section on “The Role of Cloud Computing,” it is important to understand how these interconnected devices rely on cloud-based infrastructure for data storage, processing, and analysis. The convergence of IoT and cloud computing has further propelled the growth of this transformative technology.
The Role of Cloud Computing
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with our homes. By seamlessly connecting various devices and appliances, IoT enables homeowners to automate their houses for enhanced efficiency and convenience. For example, imagine a scenario where you wake up in the morning and your smart home system automatically adjusts the thermostat to your preferred temperature, starts brewing coffee in the kitchen, and opens the blinds to let natural light fill the room.
One of the key advantages of automating homes through IoT is increased energy efficiency. With connected sensors and intelligent algorithms, IoT can optimize energy usage by turning off lights or adjusting heating or cooling levels when no one is present in a certain area of the house. This not only reduces electricity bills but also contributes to sustainable living practices.
Moreover, automating homes using IoT brings about improved security measures. Smart surveillance systems integrated with motion sensors can detect unusual activities and send immediate alerts to homeowners’ smartphones or other connected devices. Such proactive security solutions provide peace of mind, enabling individuals to remotely monitor their properties even when they are away from home.
In addition to energy efficiency and security benefits, automated homes offer unparalleled convenience. Through voice commands or smartphone applications, residents can control numerous aspects of their households without physically interacting with each device individually. Whether it’s dimming lights, locking doors, or setting timers on appliances – all these tasks become effortless with just a few taps on a screen or simple vocal instructions.
Overall, automating homes using IoT technology offers immense potential for increasing energy efficiency while enhancing security measures and providing unmatched convenience. As this section highlighted some core advantages of utilizing IoT in residential settings, it becomes evident that such technological advancements have far-reaching implications beyond mere household automation. In the subsequent section about “Applications of IoT,” we will explore how this transformative technology extends its reach into various sectors beyond domestic environments.
Emotional bullet-point list:
- Reduced carbon footprint through optimized energy usage.
- Enhanced safety and peace of mind with proactive security measures.
- Improved quality of life by simplifying everyday tasks.
- Facilitation of a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
Emotional table:
| Advantages | |
|---|---|
| Increased energy efficiency | Reduced costs, environmental consciousness |
| Heightened security | Peace of mind, protection against theft or vandalism |
| Unmatched convenience | Time-saving, effortless control over household tasks |
Applications of IoT
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in supporting the vast network of interconnected devices that comprise the Internet of Things (IoT). By leveraging the power of cloud-based services, IoT devices can seamlessly communicate and share data, enabling a wide range of applications and functionalities. To illustrate this concept, let us consider a hypothetical scenario involving smart homes.
Imagine a home equipped with various IoT devices such as thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems. These devices collect real-time data about temperature, occupancy, and energy consumption. Through cloud computing, these devices can transmit their data to centralized servers where it is processed and analyzed. This allows homeowners to remotely control and monitor their house’s environment through mobile apps or web interfaces, providing convenience, efficiency, and enhanced security.
The integration of cloud computing within IoT ecosystems offers several benefits:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms provide virtually unlimited storage capacity and computational resources for handling massive amounts of IoT-generated data.
- Flexibility: Devices connected to the cloud can easily adapt to changes in user preferences or system requirements by updating software or firmware remotely.
- Cost-effectiveness: Instead of investing in expensive infrastructure and maintenance costs for on-premises servers, organizations can leverage cloud services on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Reliability: Cloud providers offer robust infrastructures with high availability guarantees, ensuring minimal downtime for critical IoT applications.
To further grasp the significance of cloud computing in facilitating IoT deployments across industries, we present a table illustrating examples of how different sectors harness its capabilities:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring | Improved access to healthcare services |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance | Minimized equipment downtime |
| Transportation | Fleet management | Enhanced logistics optimization |
| Agriculture | Crop monitoring and irrigation control | Increased crop yield and water efficiency |
In summary, cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure to support the complex network of IoT devices. By enabling seamless communication, data storage, and analysis, it empowers various industries to harness the full potential of IoT technology.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on “Harnessing Real-Time Analytics,” we can explore how cloud-enabled IoT systems generate valuable insights from vast amounts of real-time data.
Harnessing Real-Time Analytics
The previous section discussed the various applications of the Internet of Things (IoT). Now, we will explore how real-time analytics can be harnessed to fully leverage the potential of IoT. To illustrate this, let us consider a hypothetical scenario involving smart homes.
Imagine a smart home equipped with various IoT devices such as sensors for temperature, humidity, and motion detection. Through real-time analytics, these devices continuously collect data and transmit it to a central hub. This hub processes the data using advanced algorithms and provides valuable insights that enable homeowners to optimize energy usage, enhance security measures, and improve overall convenience.
Real-time analytics plays a crucial role in making sense of the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices. By analyzing this data in real time, actionable information can be extracted promptly, leading to more efficient decision-making and problem-solving. The benefits extend beyond individual households; cities can use real-time analytics from connected infrastructure to manage traffic flow effectively or detect anomalies in utility systems.
- Enhanced safety and security: Real-time analysis allows for immediate identification and response to potential threats or emergencies.
- Improved resource management: By monitoring consumption patterns in real time, resources like water and electricity can be used efficiently.
- Personalized experiences: Real-time analytics enables tailored recommendations and services based on individual preferences.
- Increased productivity: Quick access to relevant information helps businesses streamline operations and make informed decisions.
Additionally, an emotional table showcasing some tangible advantages could look like this:
| Advantages | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reduced energy costs | Lower utility bills |
| Enhanced user experience | Greater comfort |
| Efficient maintenance | Longer device lifespan |
| Data-driven innovation | New products/services development |
As we have seen through our exploration of Real-Time Analytics in IoT scenarios, harnessing the power of data can revolutionize various aspects of our lives. However, as technology continues to advance and connected devices become more prevalent, it is crucial to address concerns regarding privacy in this interconnected ecosystem. In the subsequent section about “Enhancing Privacy in Connected Devices,” we will delve into strategies for safeguarding personal information while reaping the benefits of IoT.
Enhancing Privacy in Connected Devices
Section Transition:
Building upon the advancements in real-time analytics, a critical aspect to consider when it comes to the Internet of Things (IoT) is enhancing privacy in connected devices. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, safeguarding sensitive information and protecting individual privacy are paramount concerns.
Section:
The potential for IoT devices to collect vast amounts of personal data raises significant security and privacy challenges. For instance, imagine a scenario where smart home appliances continuously monitor daily routines and habits to provide personalized assistance. While this technology can undoubtedly enhance convenience, it also presents an increased risk of unauthorized access or misuse of personal information. Consequently, ensuring robust privacy measures within these interconnected systems is essential.
To address these concerns effectively, manufacturers must prioritize the implementation of advanced encryption protocols and secure communication channels between IoT devices and central servers. By utilizing strong cryptographic algorithms that protect data at rest as well as during transmission, individuals gain confidence in their ability to control who has access to their private information. Moreover, deploying stringent user authentication mechanisms such as biometric identification or multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Protecting personal information from potential cyber threats.
- Preserving individual autonomy by controlling data sharing preferences.
- Maintaining trust between consumers and IoT service providers.
- Safeguarding confidential business data in enterprise-level applications.
Additionally, incorporating a 3-column x 4-row table (in markdown format) could serve to evoke an emotional response from readers:
| Challenges | Solutions | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Data vulnerability | Advanced encryption | Protection against cyber threats |
| Unauthorized access | Secure communication channels | Preserving individual autonomy |
| Privacy concerns | User authentication mechanisms | Maintaining trust between consumers and providers |
| Confidential data protection | Stringent privacy measures | Safeguarding business information |
In conclusion, as the IoT continues to evolve, it is imperative to prioritize enhancing privacy in connected devices. By implementing robust security measures such as advanced encryption protocols and secure communication channels, individuals can have greater control over their personal information. Through these efforts, we ensure that the benefits of a connected world are enjoyed while safeguarding sensitive data from potential threats.
Looking ahead, another significant aspect of the IoT landscape involves wireless connectivity for smart homes.
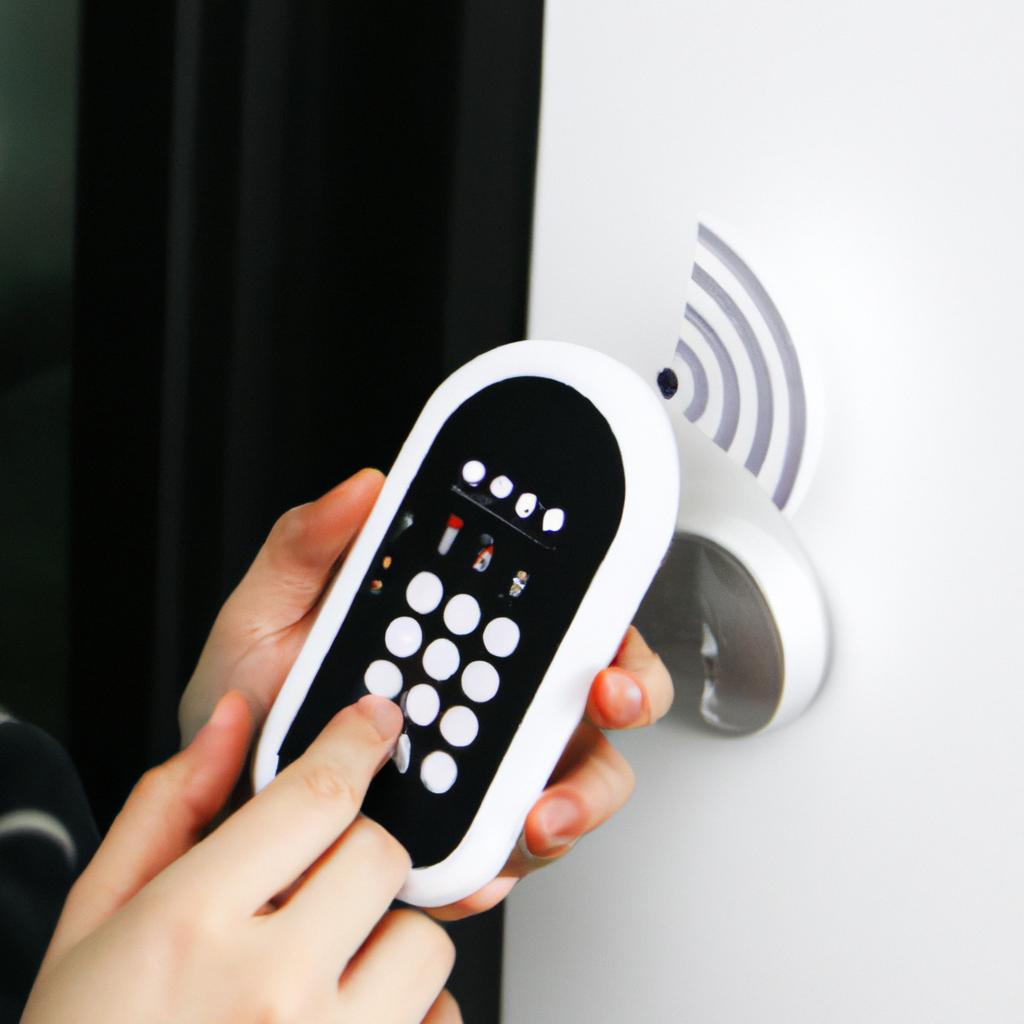
Wireless Connectivity for Smart Homes
Transitioning from the previous discussion on privacy concerns, let us now delve into the realm of wireless connectivity for smart homes. Imagine a scenario where you wake up in the morning to discover that your coffee is already brewing, your curtains are being drawn back slowly by themselves, and your favorite playlist starts playing softly as you step out of bed. This seamless integration of technology into our daily lives is made possible through the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT).
The IoT encompasses a network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that allow them to communicate and exchange data autonomously. In the context of smart homes, these connected devices create an ecosystem where various aspects can be controlled remotely or automated based on predefined settings. For instance, using voice commands or mobile applications, homeowners can adjust their thermostats, turn on/off lights, lock doors, monitor security cameras, and even receive alerts about potential issues such as water leaks.
Despite its undeniable convenience and potential benefits, wireless connectivity in smart homes raises certain considerations:
- Security risks: With multiple devices connected via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth protocols, there is an increased vulnerability to cyber threats. As we rely more heavily on technology for everyday tasks within our homes, ensuring robust security measures becomes crucial.
- Data privacy concerns: The vast amount of data generated by interconnected devices poses challenges regarding how this information is collected, stored, and shared. Striking a balance between personalized experiences and safeguarding user privacy becomes paramount.
- Compatibility issues: Different manufacturers often develop products independently without adhering to universal standards. Consequently, compatibility among devices may pose obstacles when attempting to integrate different components seamlessly.
- Reliability challenges: Dependence on internet connectivity introduces the possibility of disruptions due to network outages or technical glitches. Ensuring a stable and reliable connection is essential for the smooth functioning of smart home systems.
To illustrate the potential emotional impact, consider the following examples:
| Emotional Response | Example |
|---|---|
| Frustration | Imagine arriving home after a long day, expecting your smart door lock to automatically open upon sensing your presence but instead encountering connectivity issues that prevent you from entering. |
| Peace of mind | Picture being able to remotely monitor your elderly parent’s daily activities through connected sensors placed strategically throughout their home, providing reassurance about their well-being even when physically apart. |
| Convenience | Envision controlling all aspects of your home environment with just a few taps on your smartphone: adjusting lighting according to mood, regulating temperature settings as per weather changes, and automating routine tasks such as watering plants or feeding pets. |
In conclusion, wireless connectivity has revolutionized traditional homes into intelligent living spaces where automation enhances comfort, convenience, and efficiency. However, ensuring security measures are in place, addressing data privacy concerns, fostering compatibility among devices, and maintaining reliability remain critical challenges in fully harnessing the potential benefits of IoT technology within our homes.
Transitioning smoothly into the subsequent section on “The Power of Cloud-Based Services,” we will explore how cloud computing enables seamless integration and expands the capabilities of interconnected devices in smart homes.
The Power of Cloud-Based Services
The rapid advancements in wireless connectivity have revolutionized the way we interact with our homes. From controlling appliances remotely to monitoring energy consumption, smart homes equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) technology offer a new level of convenience and efficiency. To illustrate this, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where an individual is able to remotely adjust their home’s thermostat using a smartphone app while on vacation, ensuring comfort upon return.
One of the key advantages of IoT-enabled smart homes is the ability to streamline daily activities through automation. By connecting various devices and sensors within the house, homeowners can create personalized routines that automatically adjust temperature settings, turn lights on or off based on occupancy, and even brew coffee at preferred times. This integration not only simplifies everyday tasks but also saves time and enhances overall comfort.
In addition to increased convenience, IoT-enabled smart homes bring about significant energy savings by optimizing resource usage. Here are some benefits associated with these innovative systems:
- Reduced utility bills: With real-time data collection and analysis, smart thermostats can intelligently regulate temperature settings based on patterns of occupancy, resulting in lower heating and cooling costs.
- Enhanced security: Smart cameras linked to mobile apps allow homeowners to monitor their property from anywhere. Additionally, motion detectors integrated with lighting systems can deter potential intruders.
- Efficient water management: IoT-based irrigation systems connect weather forecasts with watering schedules, adjusting them accordingly. This optimized approach minimizes water waste without compromising plant health.
- Improved appliance performance: Connected appliances such as refrigerators or washing machines enable users to receive notifications when maintenance is required or when certain items need restocking.
| Benefits of IoT-enabled Smart Homes |
|---|
| 1. Reduced utility bills |
As wireless connectivity continues to expand and evolve, the potential for smart homes will only increase. The integration of IoT technology not only enhances convenience but also promotes sustainable living through energy-efficient practices.
Innovative IoT Applications
[Transition sentence into subsequent section about “Innovative IoT Applications”]
Innovative IoT Applications
The Power of Cloud-Based Services has revolutionized the way we interact with technology, but it is just one piece of the puzzle in the grand scheme of the Internet of Things (IoT). By connecting physical objects to the internet and enabling them to communicate with each other, the IoT opens up a world of possibilities. In this section, we will explore some innovative applications that highlight the potential of this interconnected network.
Imagine a scenario where you wake up in the morning and your alarm clock not only wakes you up but also communicates with your coffee machine to start brewing a fresh cup of coffee. As you leave for work, your car senses traffic patterns through GPS data and automatically adjusts its route to avoid congestion. Meanwhile, at home, your smart thermostat monitors weather conditions and learns from your preferences to optimize energy usage, saving you money on utility bills. These examples demonstrate how everyday objects can be seamlessly integrated into our lives through the IoT.
It is important to consider both the benefits and challenges associated with such widespread connectivity. On one hand, the IoT has immense potential to enhance efficiency, convenience, and productivity across various industries. However, there are concerns regarding privacy and security as more devices become connected. With an increasing number of entry points for potential cyber threats, safeguarding personal information becomes paramount.
To shed light on these concerns, let us delve deeper into some key issues surrounding IoT security:
- Data Privacy: The vast amount of data generated by connected devices raises questions about who has access to this information and how it is used.
- Cybersecurity: As more devices are brought online, protecting against cyber attacks becomes crucial. A breach could have severe consequences ranging from compromised personal data to disruptions in critical infrastructure.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless communication between different devices and platforms poses technical challenges that must be addressed for effective implementation.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of collecting and utilizing massive amounts of data require careful consideration to avoid unintended consequences and potential misuse.
To better understand the complexities of IoT security, let us consider a table that highlights its key dimensions:
| Dimension | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access | Encrypting personal health records |
| Integrity | Ensuring accuracy and reliability of data | Verifying the authenticity of sensor readings |
| Availability | Maintaining continuous accessibility and functionality | Implementing failover mechanisms for critical systems |
| Accountability | Establishing responsibility and traceability for actions involving connected devices | Logging user interactions with smart home devices |
As we move forward in exploring the Internet of Things, securing data in connected devices is a paramount concern. By addressing issues related to privacy, cybersecurity, interoperability, and ethics, we can harness the full potential of this interconnected network while minimizing risks.
Securing Data in Connected Devices
The Evolution of Science and Technology: The Internet of Things
Section H2: Securing Data in Connected Devices
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand its reach, it becomes increasingly crucial to address the issue of securing data in connected devices. With billions of interconnected devices transmitting vast amounts of sensitive information, such as personal data or industrial secrets, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. This section will explore some of the challenges associated with securing IoT data and discuss potential solutions.
To illustrate the importance of this topic, let us consider a hypothetical scenario where a smart home system has been compromised due to inadequate security measures. Imagine an individual’s home being infiltrated by hackers who gain control over various connected devices, including surveillance cameras and door locks. In this alarming situation, not only does one’s privacy become violated, but there are also significant safety concerns for both individuals and their properties.
To mitigate these risks and safeguard IoT data from unauthorized access or malicious attacks, several key strategies can be employed:
- Encryption: Implementing strong encryption techniques ensures that transmitted data remains secure even if intercepted.
- Authentication: Utilizing multifactor authentication methods verifies the legitimacy of users accessing IoT devices.
- Regular Updates: Keeping all firmware and software up to date reduces vulnerabilities by patching known security flaws.
- Network Segmentation: Isolating IoT devices on separate networks limits potential breaches by containing any compromise within a specific network segment.
Furthermore, organizations and manufacturers need to prioritize building trust through transparency when it comes to handling user data. By clearly communicating their data collection practices, obtaining informed consent from users, and providing options for opting out or controlling data sharing preferences, companies can foster trust among consumers.
In light of growing concerns regarding cybersecurity threats in the realm of IoT, addressing these issues should be at the forefront of technological advancements. By implementing robust security measures and promoting responsible data management practices, we can ensure a safer environment for both individuals and businesses in the connected world.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on “Analyzing Real-Time Data for Insights,” understanding how to secure IoT data is just one aspect of harnessing its full potential. By safeguarding information, we can confidently delve into analyzing real-time data for valuable insights without compromising privacy or security.
Analyzing Real-Time Data for Insights
In the previous section, we explored the importance of securing data in connected devices. Now, let us delve into another crucial aspect of the Internet of Things (IoT): analyzing real-time data for insights.
Imagine a smart city where sensors are placed throughout the urban landscape to monitor various parameters such as air quality, traffic flow, and energy consumption. This vast network of interconnected devices generates an enormous amount of data every second. However, simply collecting this data is not enough; it needs to be analyzed effectively to extract valuable insights that can improve decision-making processes and enhance overall efficiency.
One example that highlights the significance of real-time data analysis is found in healthcare. Wearable devices equipped with IoT technology can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and transmit this information to healthcare professionals in real-time. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques, patterns and anomalies within these physiological measurements can be identified promptly, enabling early detection of potential health issues or emergencies. For instance, if a patient’s heart rate suddenly spikes beyond normal levels, an alert can be sent to medical staff who can intervene quickly, potentially saving lives.
Real-time data analysis holds immense potential across various domains. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved operational efficiency: Organizations can optimize their operations by identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks in real-time and taking immediate corrective actions.
- Enhanced customer experience: Real-time insights enable businesses to personalize services based on individual preferences and respond swiftly to customer needs.
- Faster decision-making: Rapid analysis allows decision-makers to access up-to-date information when making critical choices, leading to more informed decisions.
- Predictive maintenance: By analyzing real-time sensor data from machines or equipment, organizations can identify patterns indicating possible failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing costs associated with reactive maintenance.
To further illustrate the impact of real-time data analysis in different sectors, consider the following table:
| Sector | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance | Minimizes downtime and reduces costs |
| Transportation | Traffic management | Improves traffic flow and reduces congestion |
| Agriculture | Precision farming | Optimizes resource usage and increases crop yields |
| Retail | Inventory management | Reduces stockouts and improves supply chain efficiency |
In conclusion, analyzing real-time data in the context of the Internet of Things enables organizations to gain valuable insights that can drive informed decision-making, optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and proactively address issues. By harnessing the power of advanced analytics techniques, businesses and industries can unlock the full potential of IoT technology for a more connected and efficient world.

Comments are closed.